An origin of replication. Noun an extrachromosomal ring of DNA especially of bacteria that replicates autonomously.
Ti-plasmid is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found in Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
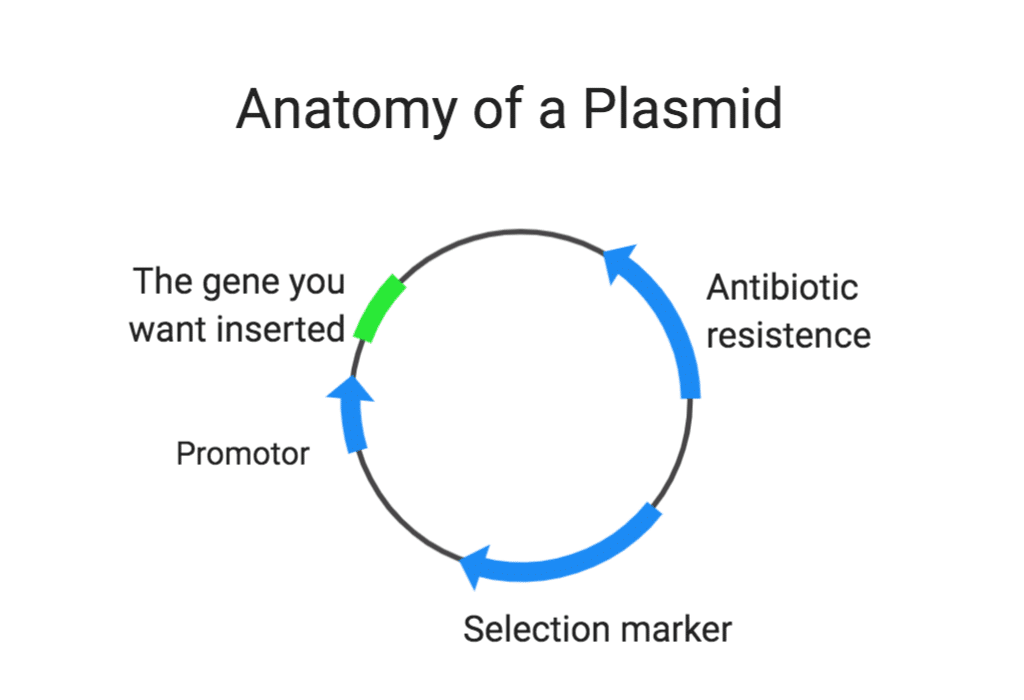
. Plasmids consist of cyclic. A small circular double stranded DNA molecule which can replicate independently from its chromosomal DNA. A plasmid is a small circular double-stranded DNA molecule that is distinct from a cells chromosomal DNA.
In the two Rhizobium. It is a pathogenic plasmid that is known to cause crown gall disease in plant cells. If plasmids are used for experiments they are called vectors.
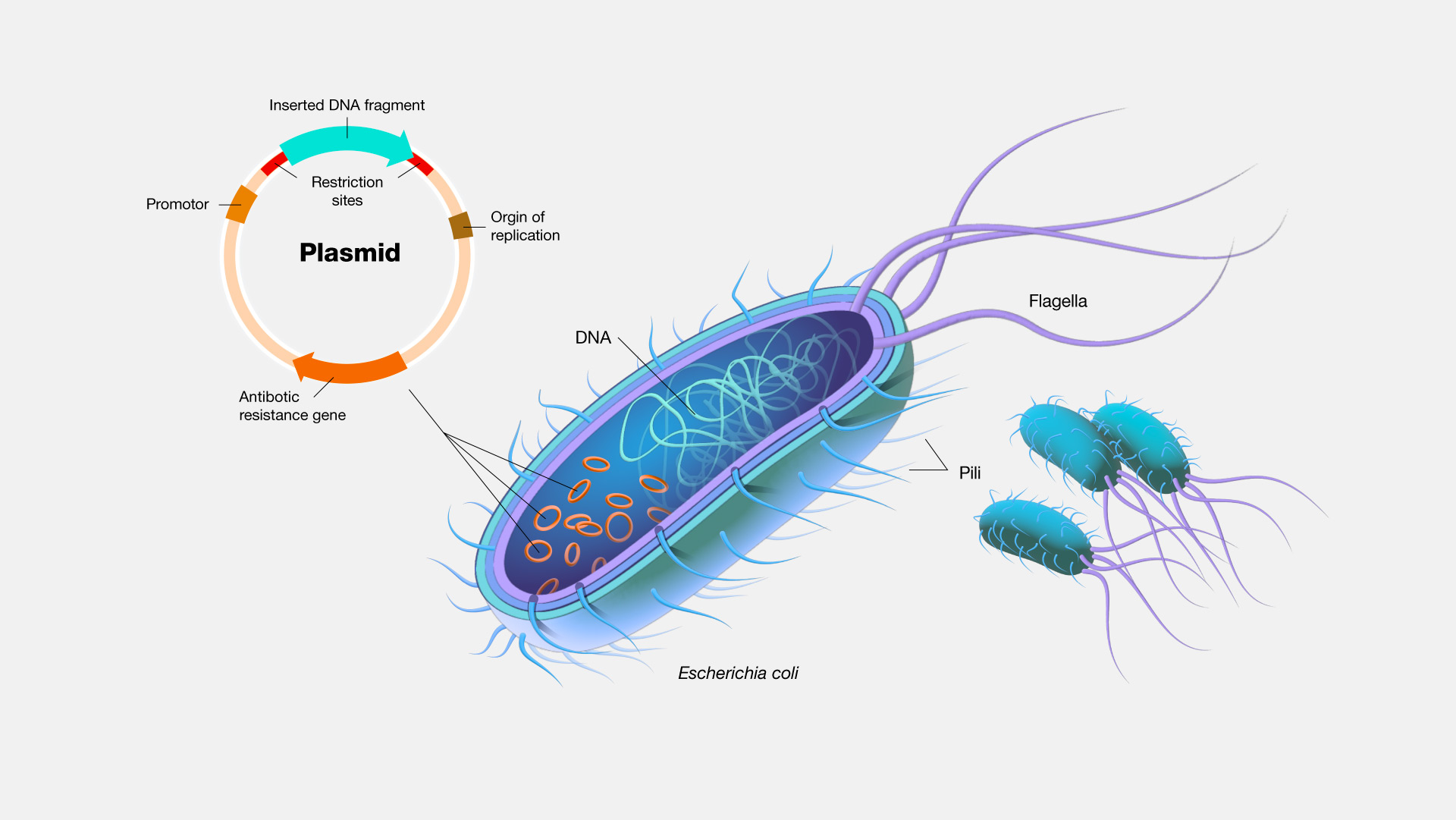
Plasmids are the most-commonly used bacterial cloning vectors. Plasmid plazmid an extrachromosomal self-replicating structure found in bacterial cells that carries genes for a variety of functions not essential for cell growth. Plasmid is small in size circular in shape and it is a piece of DNA that is not the same as chromosomal DNA.
In the two Rhizobium. Why is a plasmid considered a cloning vector. Plasmids naturally exist in bacterial cells and they also occur.
A plasmid measures up to 1 to 200 kb in size and produces enzymes that can degrade antibiotics or heavy metals. But what is a plasmid. Plasmid A is 135 Mb and plasmid B is 168 Mb.
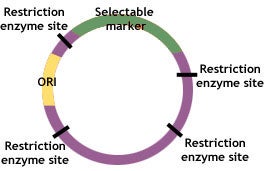
And why are they so useful to scienti. A multiple cloning site MCS containing sequences recognized by common restriction enzymes and designed to allow simple insertion of a desired gene sequence. Any life scientist working in a lab has surely heard about them.
Its ability to replicate is independent of chromosomal DNA. A plasmid is a small circular piece of DNA that is different than the chromosomal DNA which is all the genetic material found in an organisms chromosomes. There are five main types of plasmids namely fertility F-plasmids resistance.
These cloning vectors contain a site that allows DNA fragments. Plasmid A is the typical symbiotic plasmid with nod nif and fix genes whereas plasmid B has genes for exopolysaccharides required in the symbioses of this species. Plasmid A is the typical symbiotic plasmid with nod nif and fix genes whereas plasmid B has genes for exopolysaccharides required in the symbioses of this species.
These plasmids are larger than the entire genomes of many obligately symbiotic bacteria and even some free-living bacteria. Where are they found.

Why Validating Your Plasmids Is Key To A Successful Transgenic And How You Can Do It Too Invivo Biosystems

Plasmids 101 What Is A Plasmid

0 Comments